Vision System for Autonomous Navigation of Underwater Vehicles
Abstract
Remotely Operated (Underwater) Vehicles (ROVs) are increasingly being used for inspection of offshore/underwater structures. However the visual data acquired underwater is often poor in quality due lack of sufficient/uniform illumination, haze due to atmospheric light reflected by the suspended particles in the murky water, selective absorption of different wavelengths causing colour imbalance and subsequently poor contrast, etc. We propose to rectify these problems using various Dehazing and Enhancement algorithms. We also attempt to solve the problem of autonomous navigation using absolute depth maps obtained from the enhanced monocular images.
The Vision System developed first dehazes and enhances the video frame to improve the image quality which is then used for further feature extraction. To solve the problem of autonomous navigation, the use of absolute depth maps is proposed. The depth maps are used for perceiving the structure, 2D shape and third dimension depth, of the scene to detect and avoid obstacles.
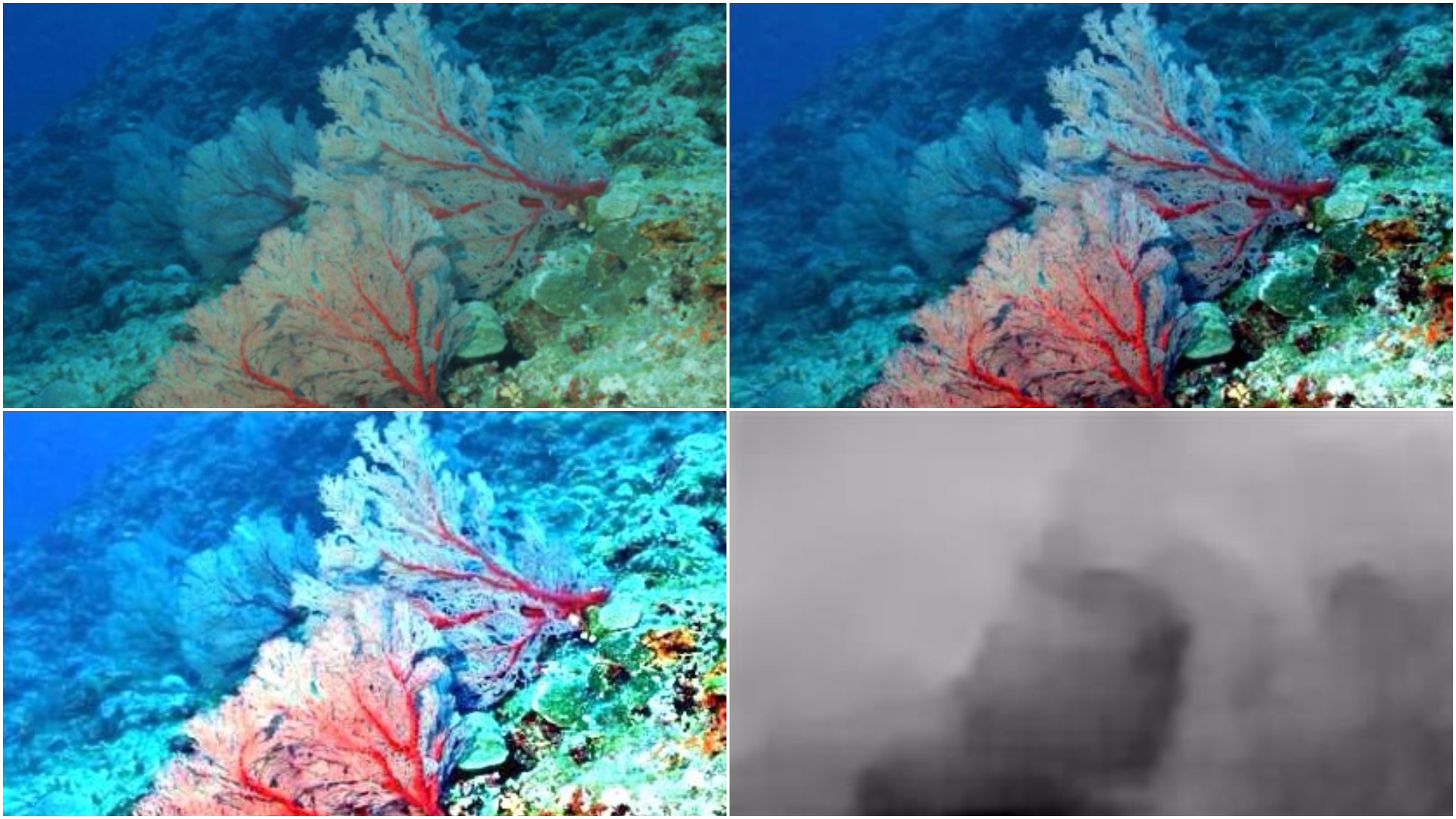
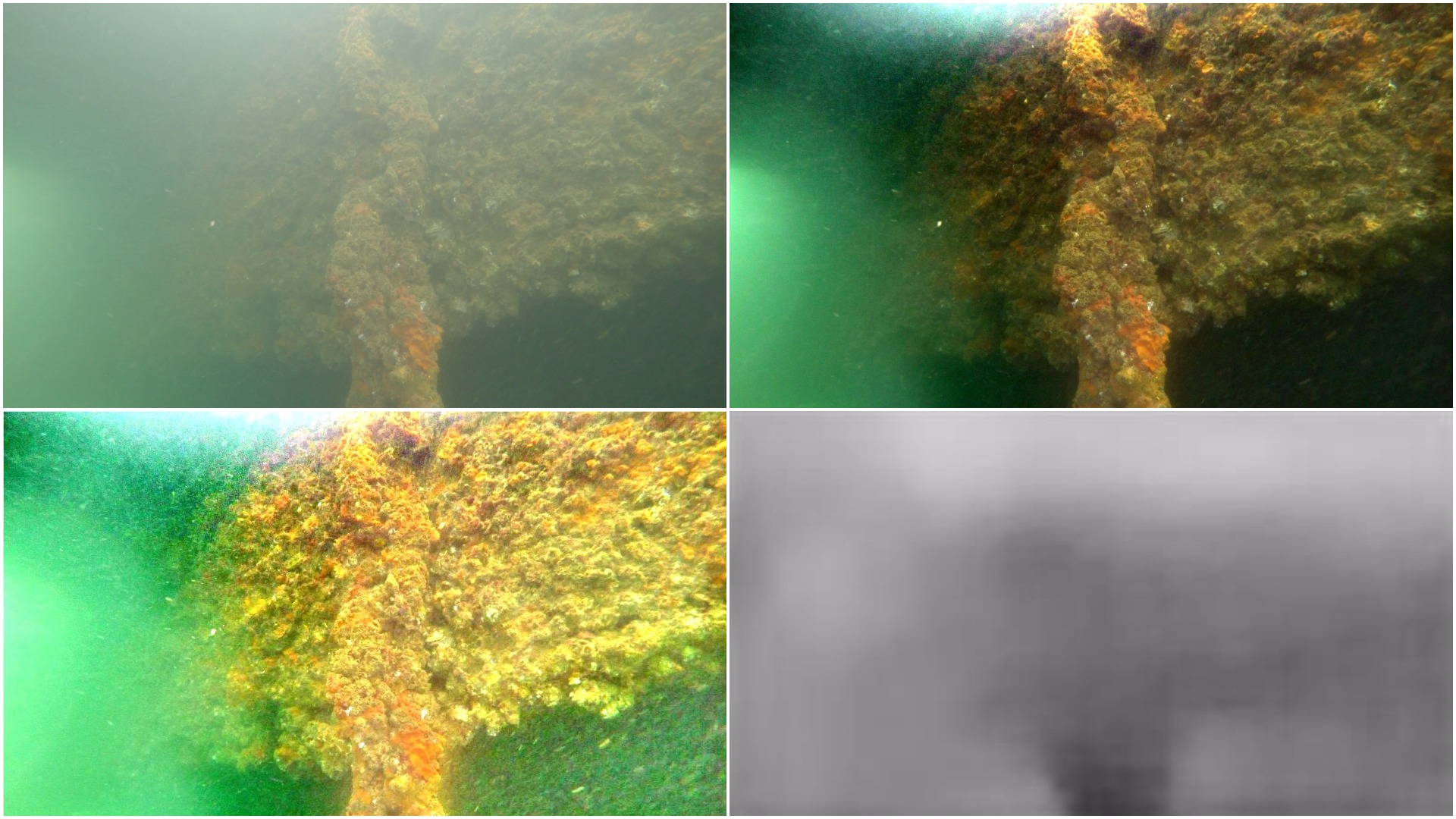
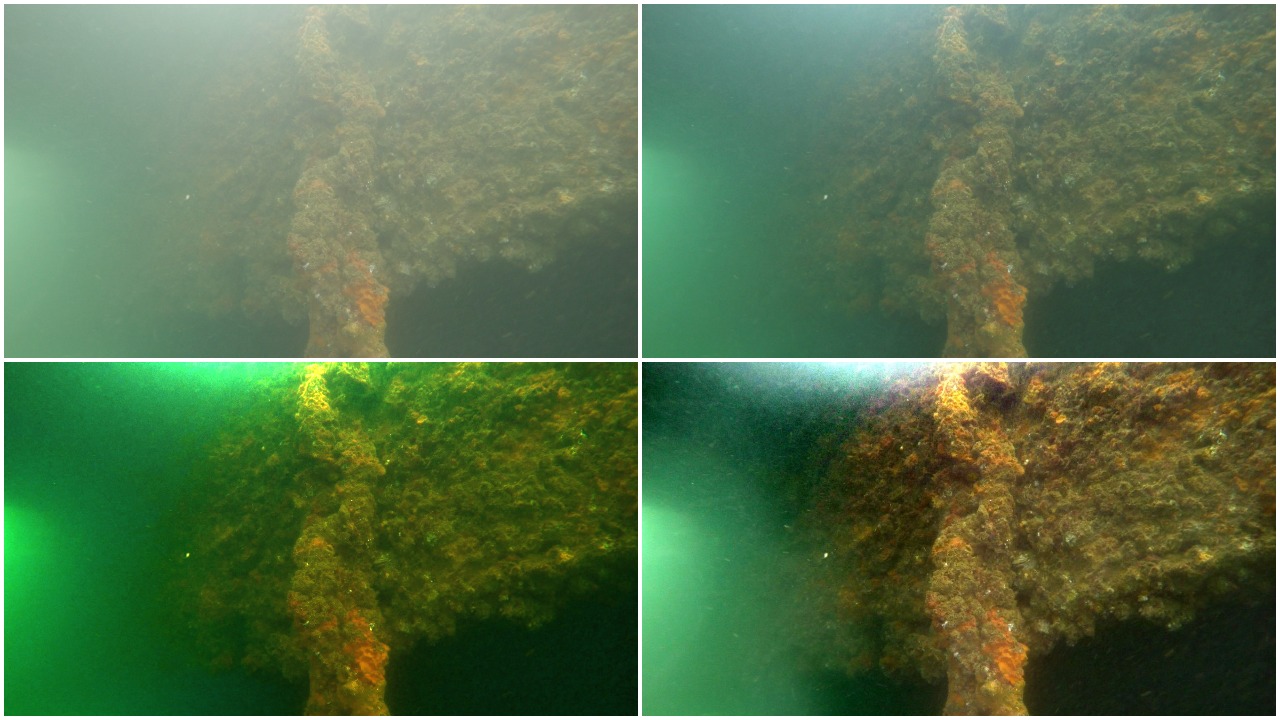
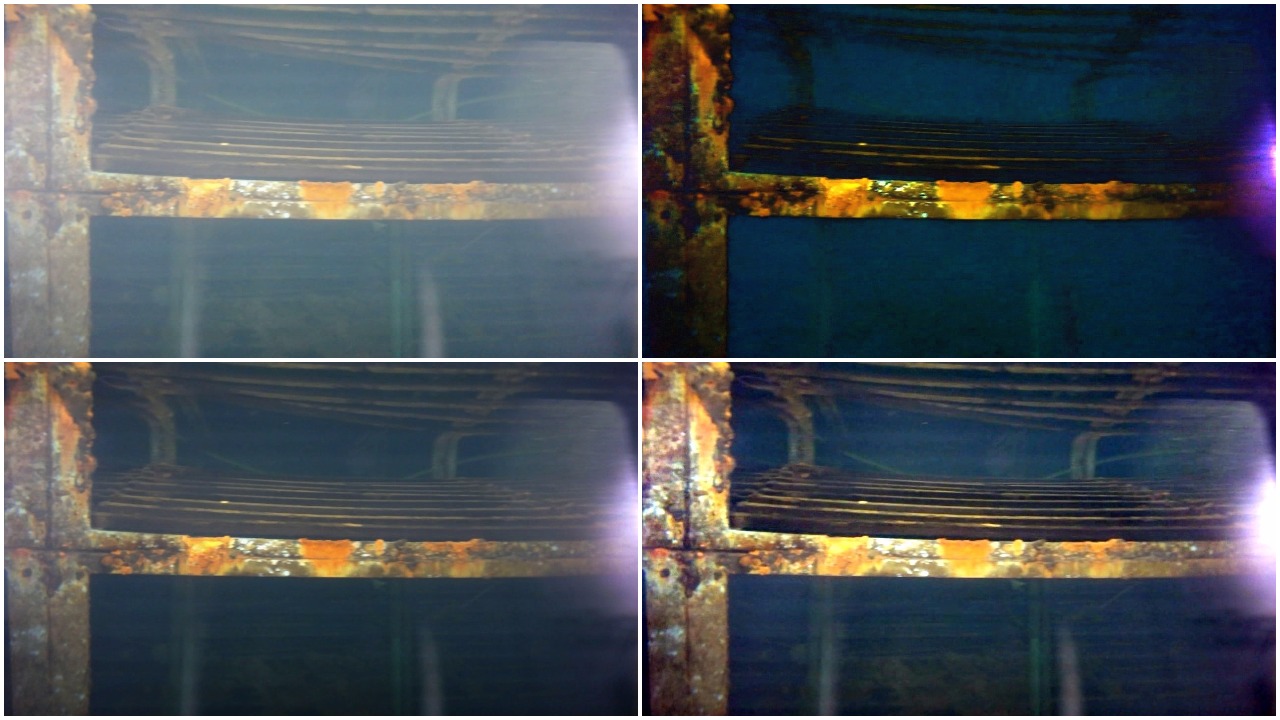
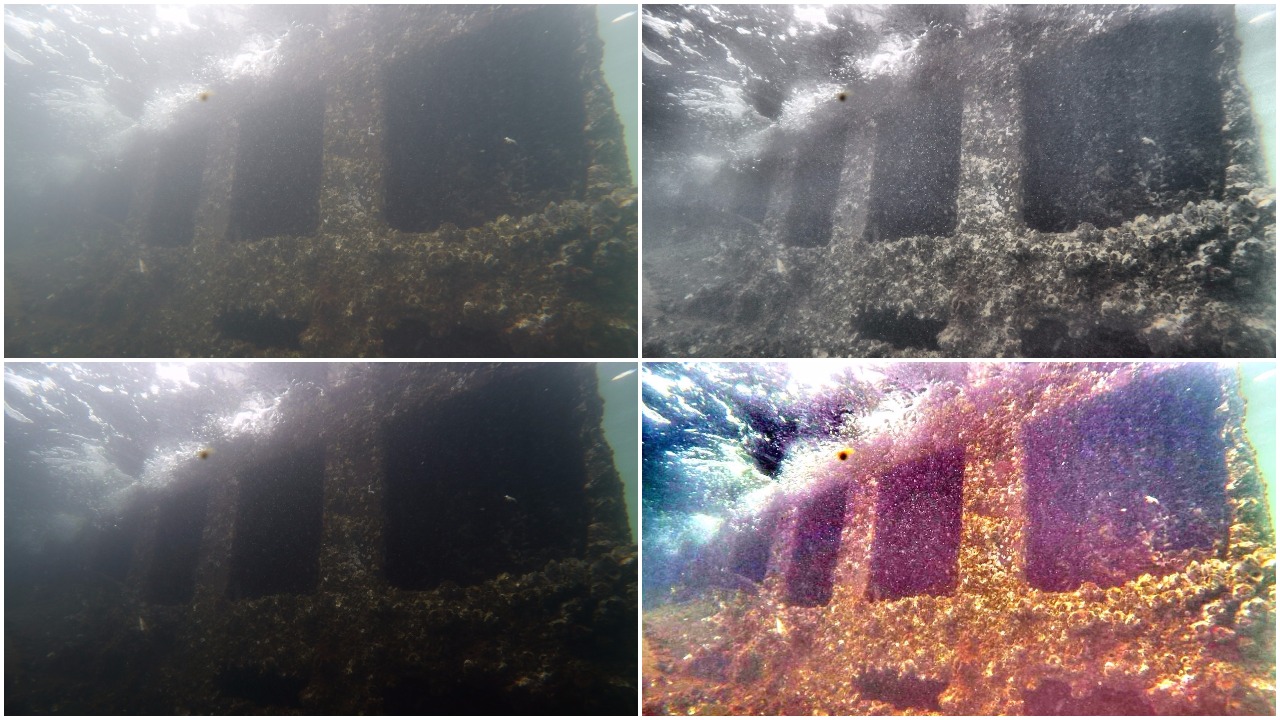
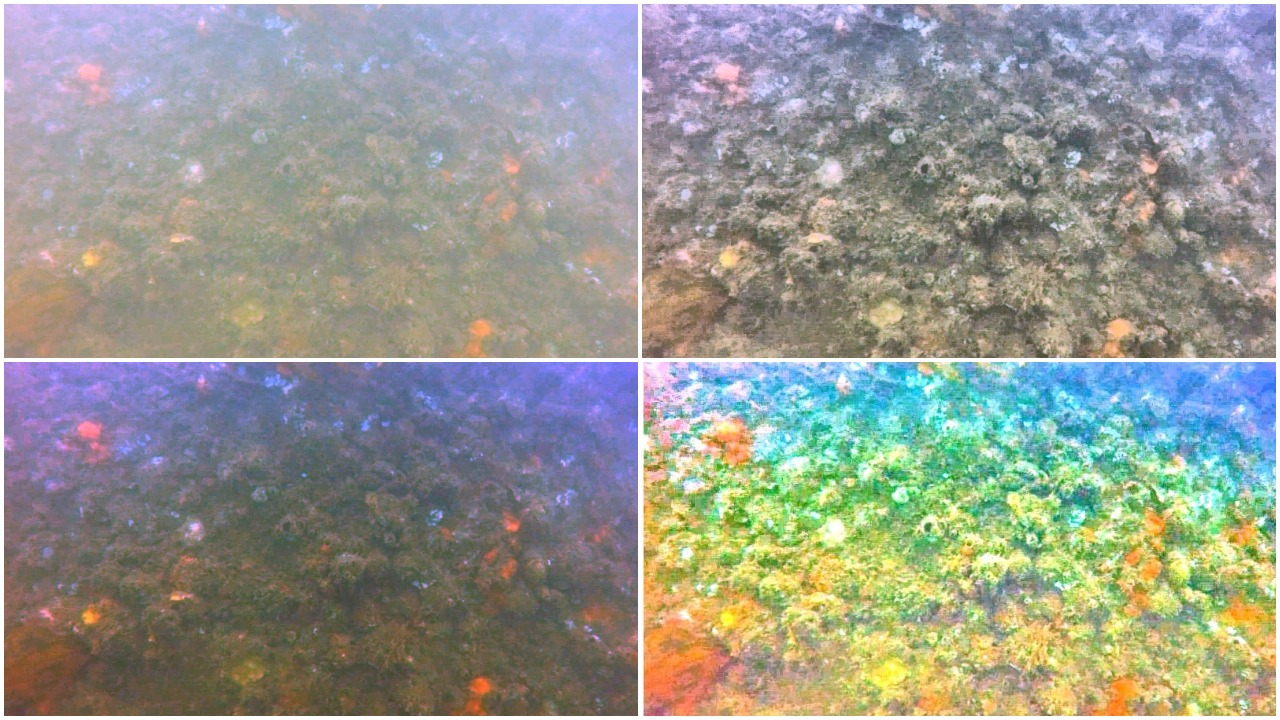
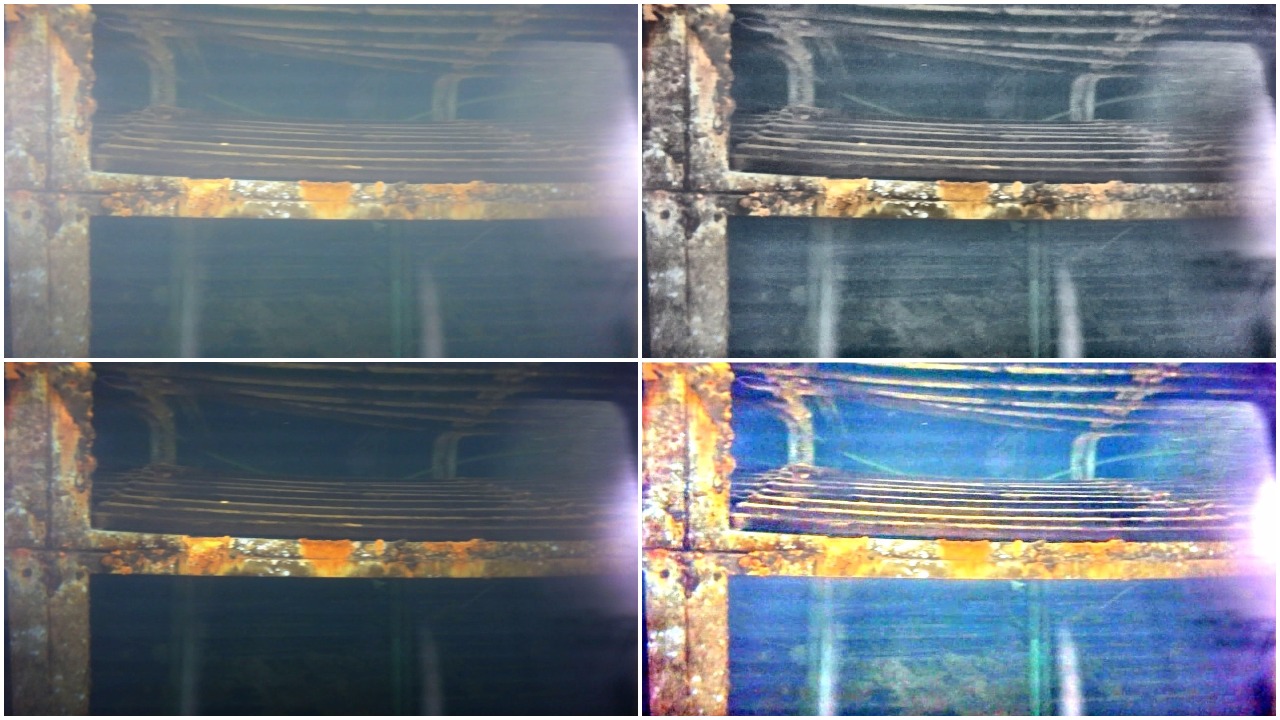
To solve the Image Dehazing problem Dark Channel Prior, Color Attenuation Prior, ConvNet based DehazeNet and Non-Local Image Dehazing algorithms were implemented and their results were compared. Using the Non-Local Image Dehazing algorithm the Contrast-toNoise Ratio (CNR) was increased by 20-50 on test images.
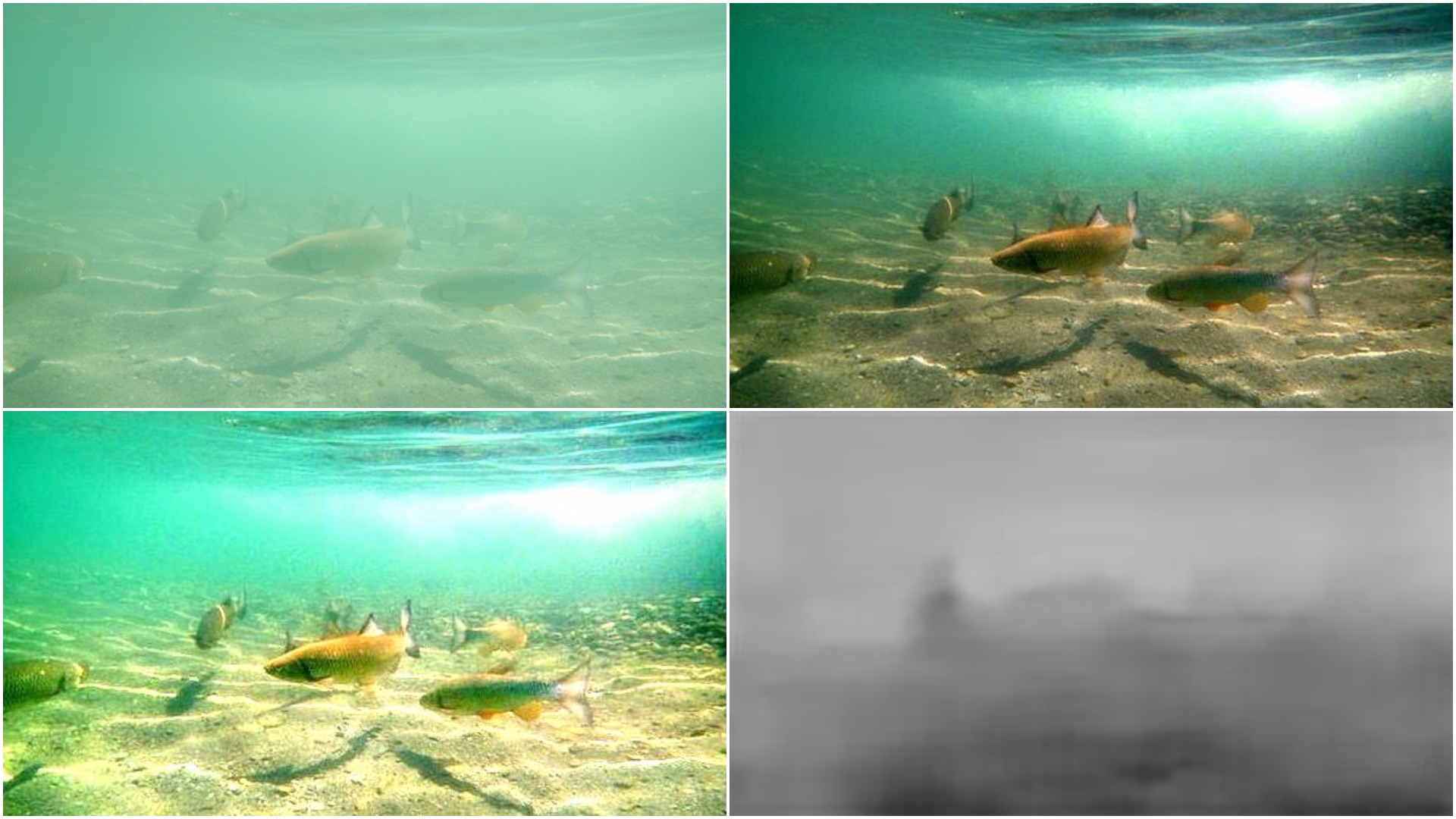
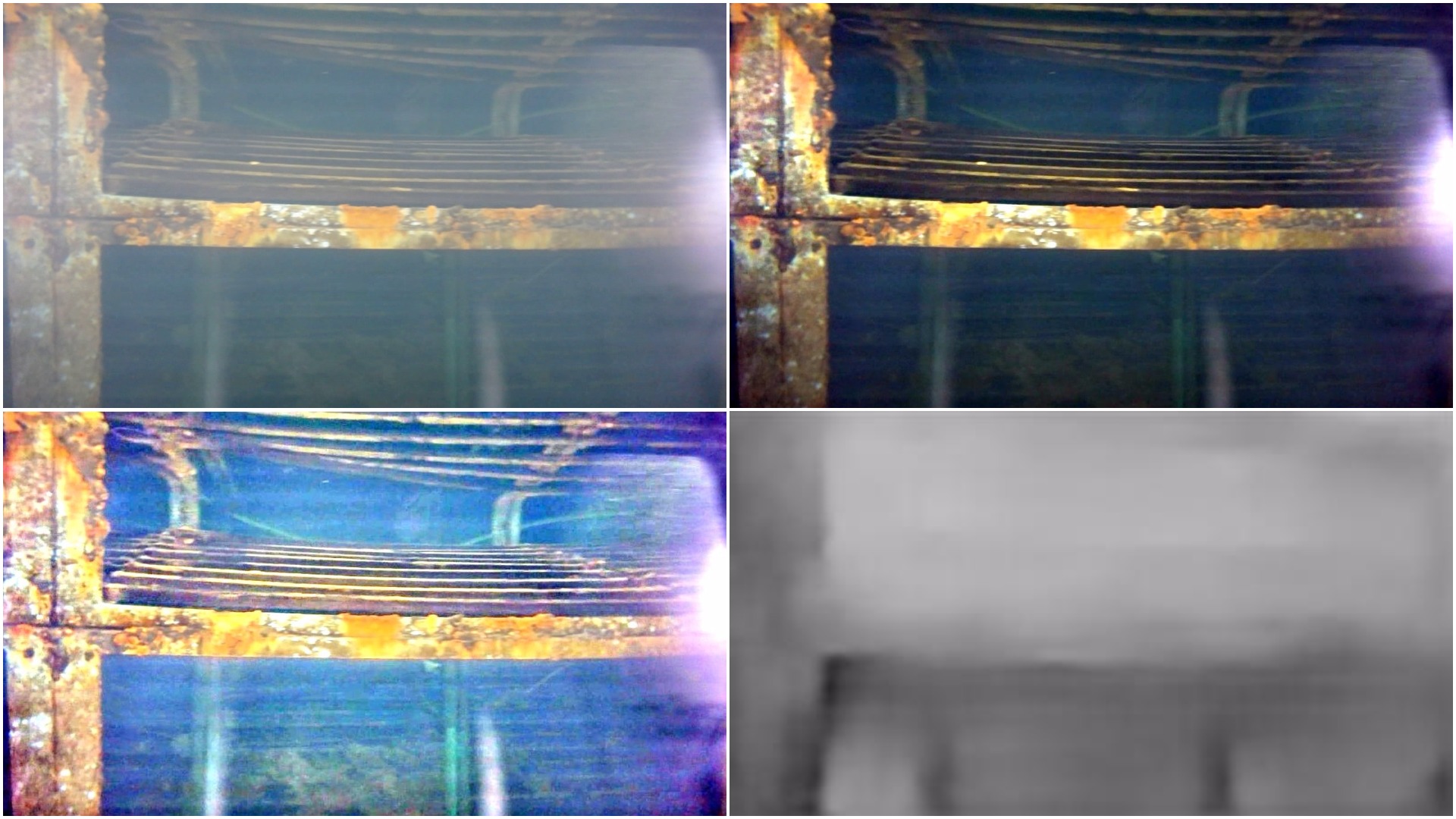
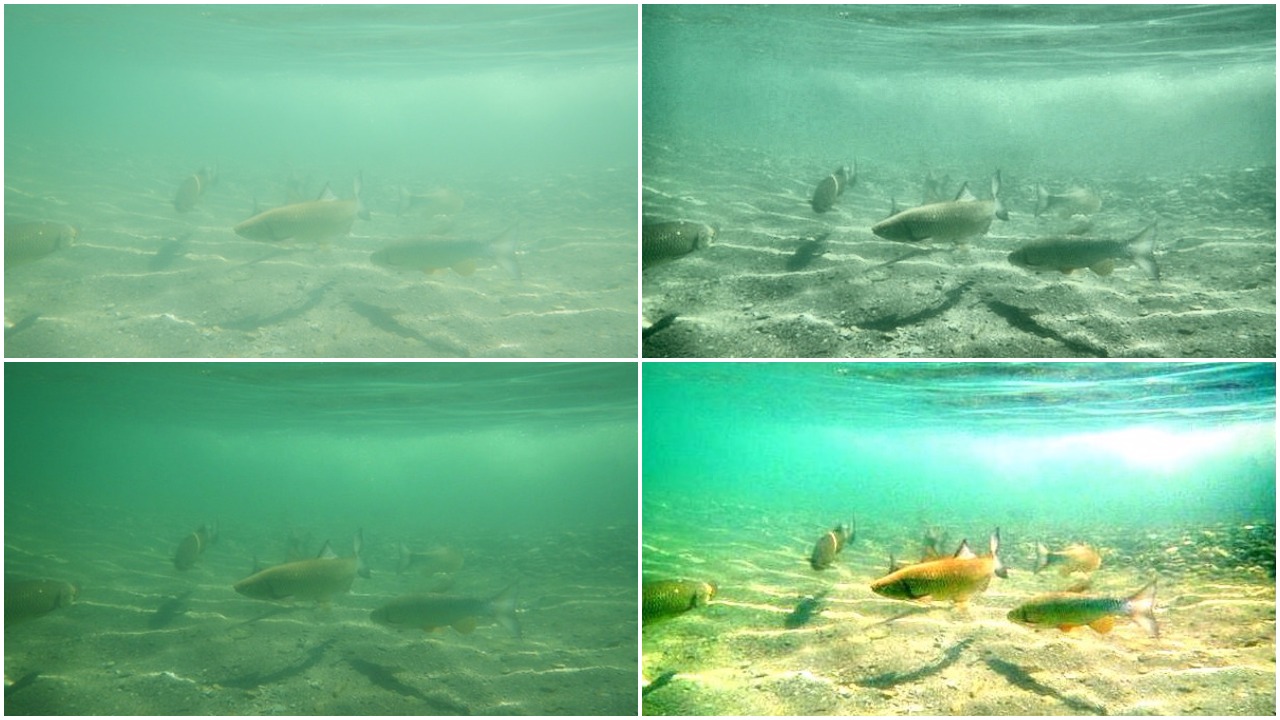
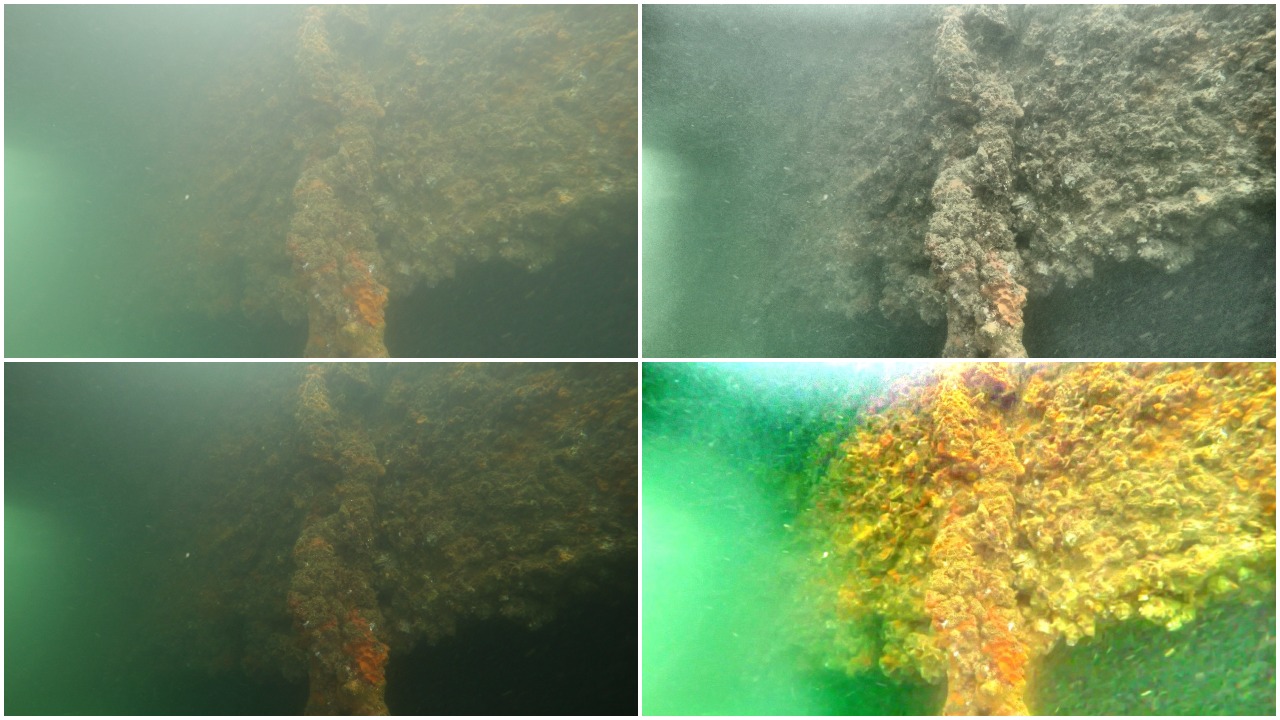
To uncover the visual cues hiding in low-light setting, Gamma Correction, CLAHE and Illumination Map Estimation based algorithm were implemented. The Illumination Map Estimation based algorithm was able to increase average local contrast by around 20-40 on test images.
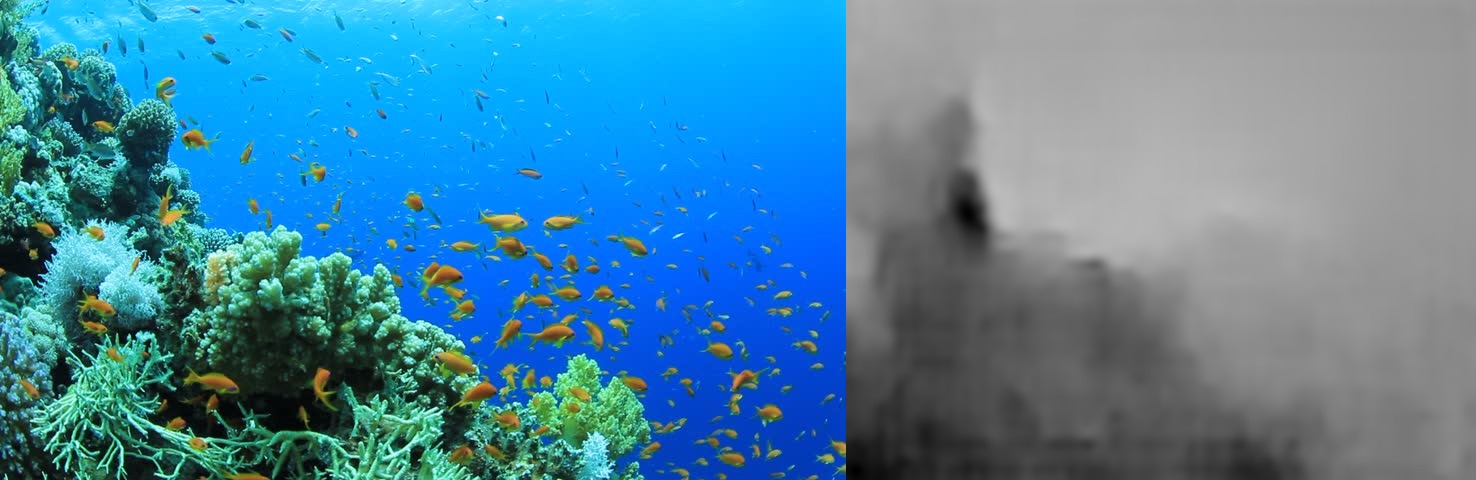
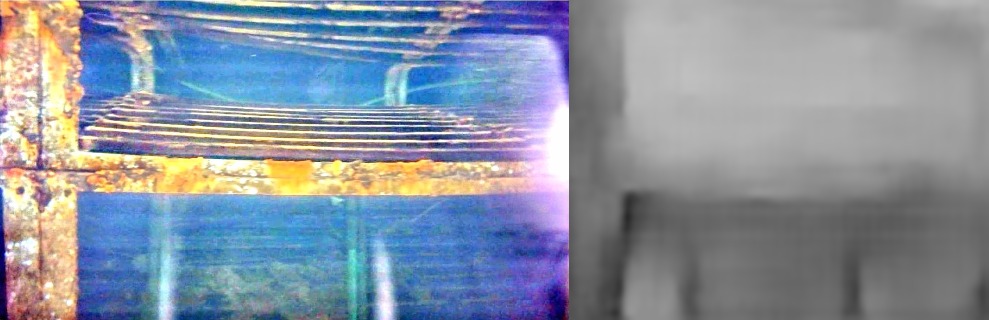
To solve the problem of autonomous navigation, we estimate the depth maps from the enhanced monocular images, we use Deep Convolutional Neural Networks to extract the depth relevant features in a fully supervised training setting. The estimated depth maps are also refined using regularization and the pixel cluster with most depth is proposed as suitable navigation direction. Finally to summarize the inspected area a framework for mosaicking video is proposed which if combined with the mosaic of depth map can provide the full three dimensional setting of the scene.
Results
Image Dehazing
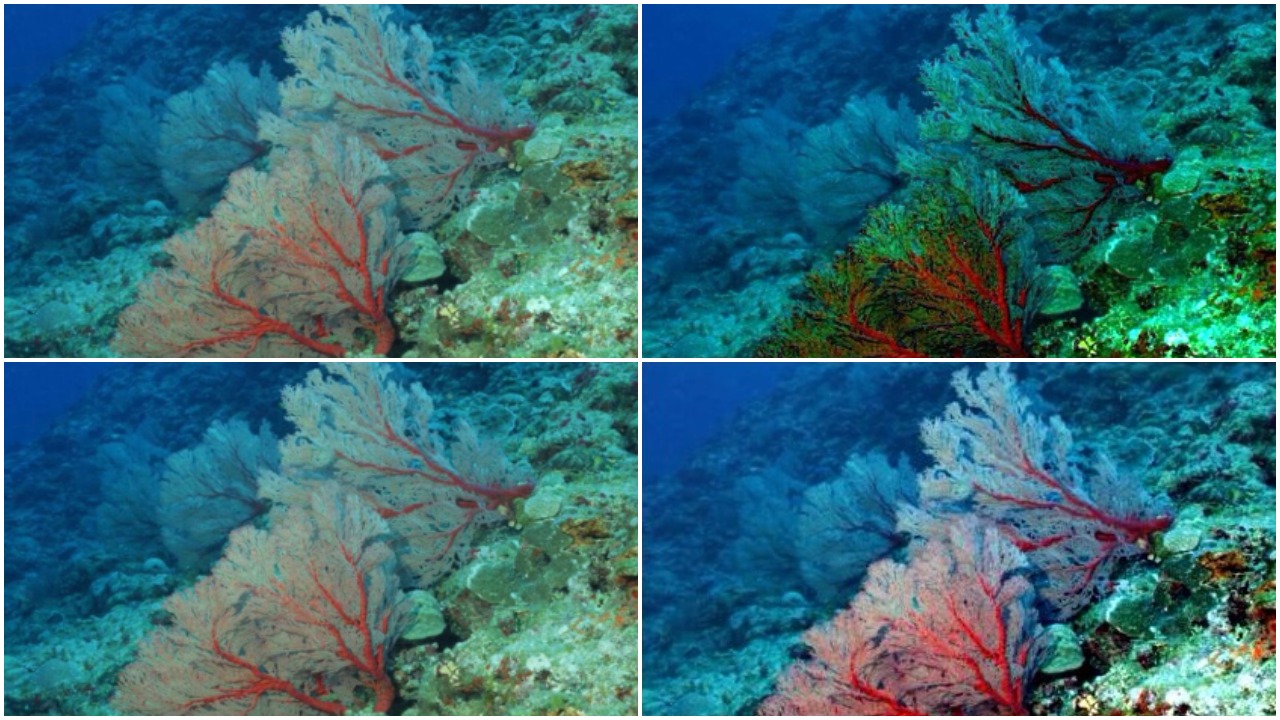
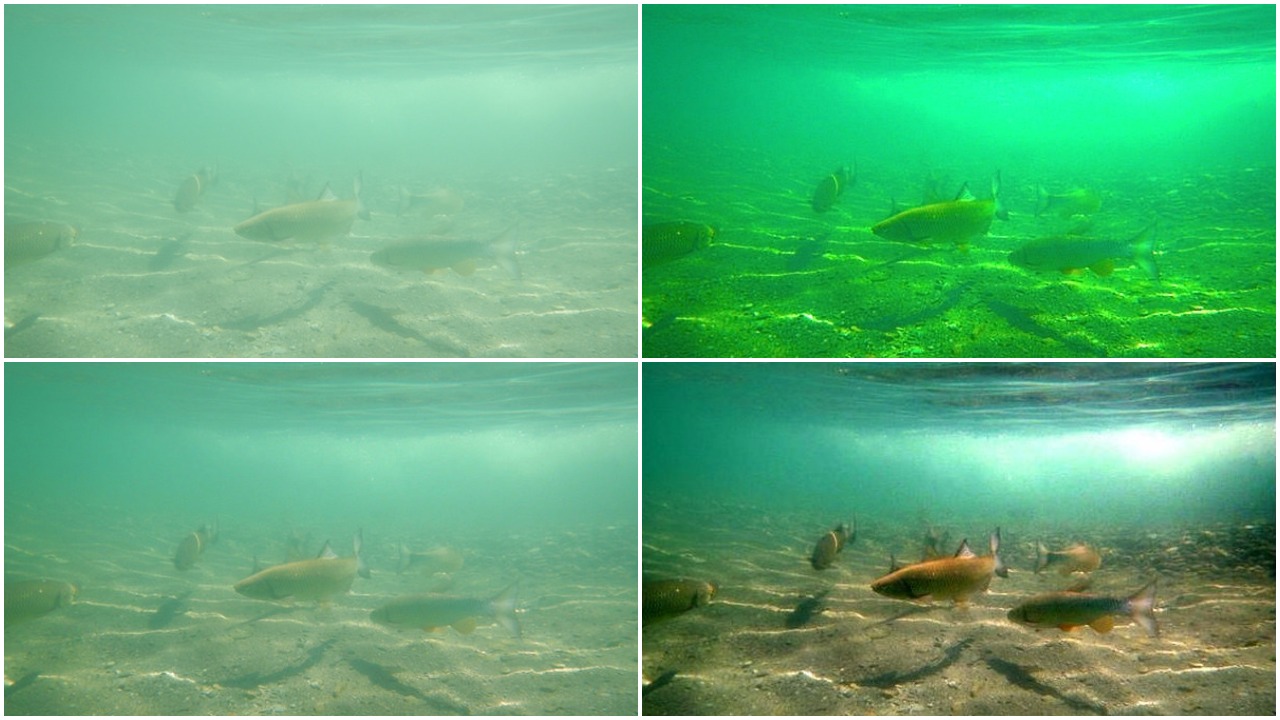
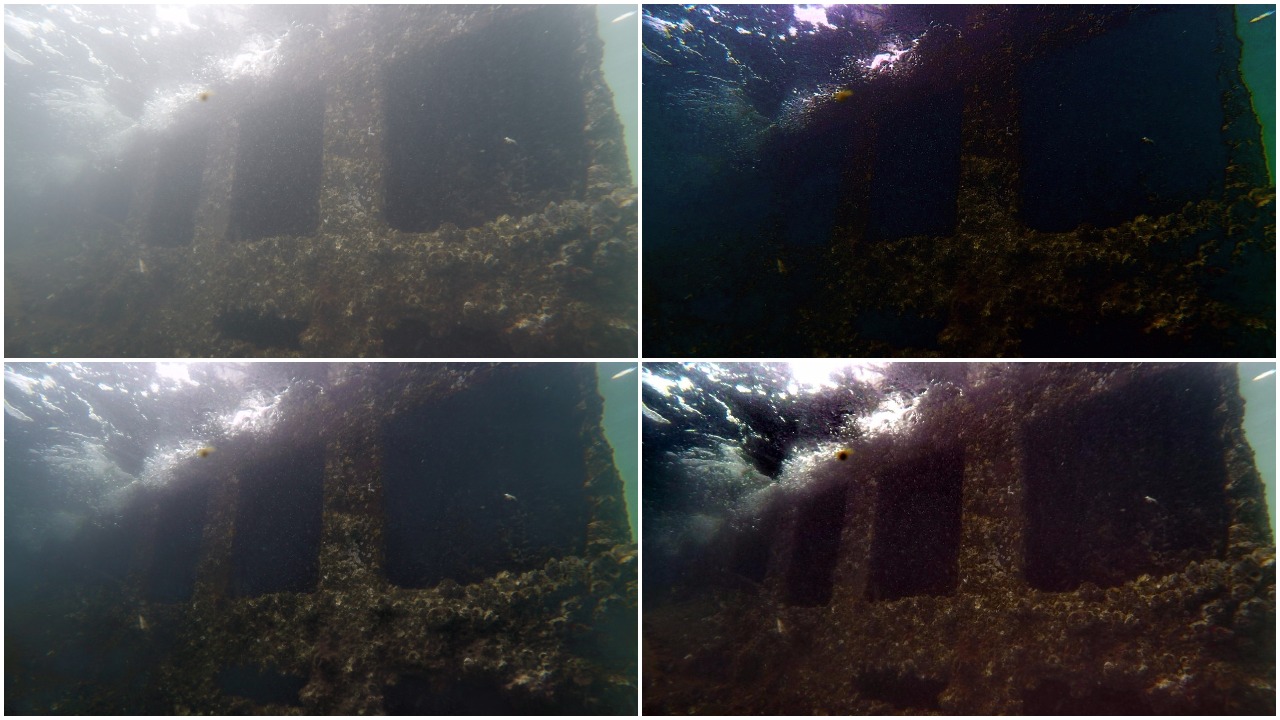

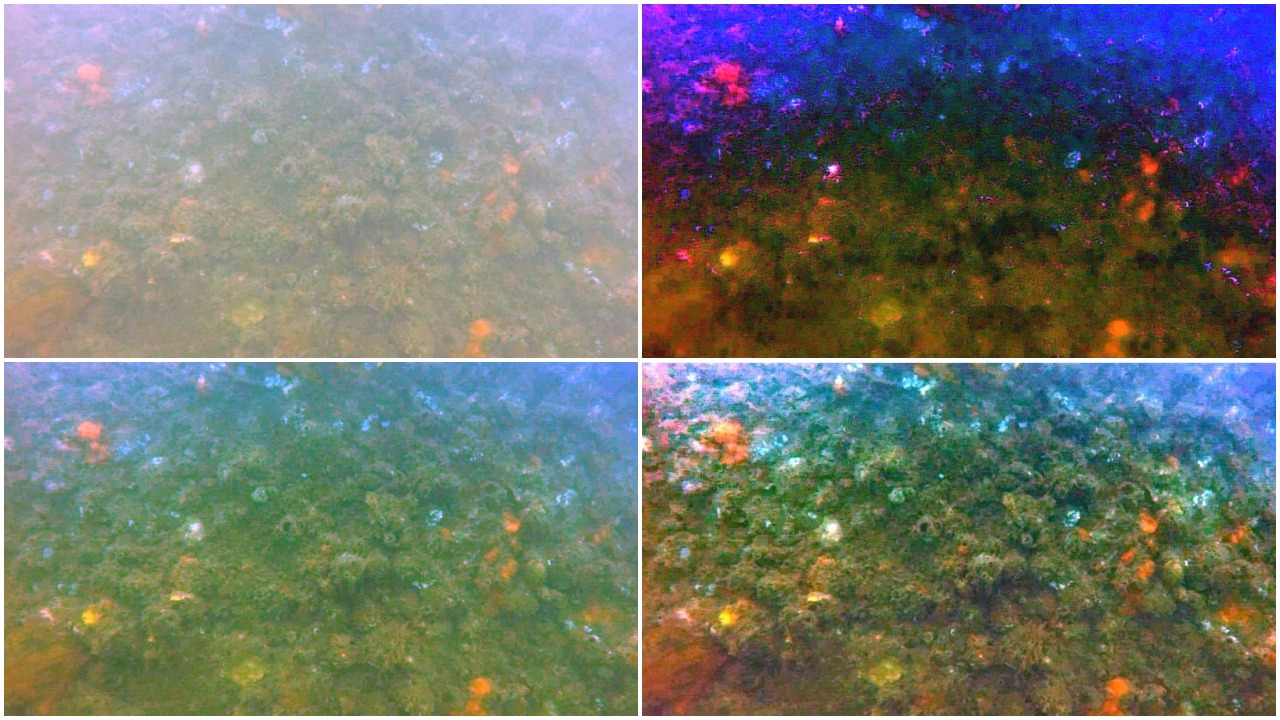

Low Light Image Enhancement




Depth Map Estimation from Single Monocular Images using Deep Convolutinal Neural Fields
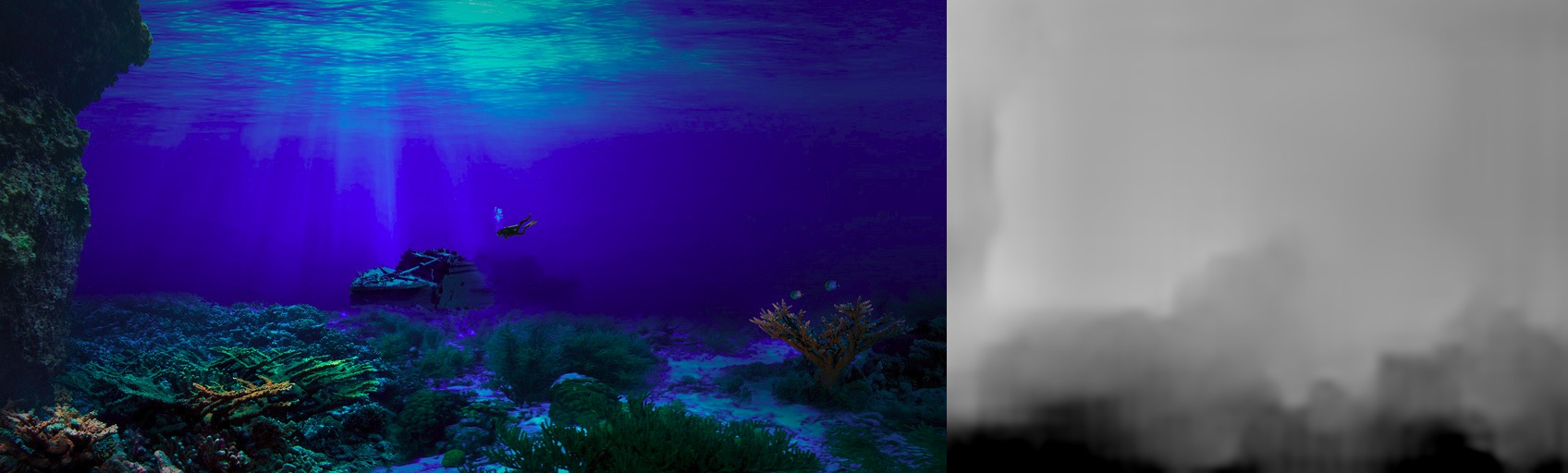












Overall